Research predicts that the long-duration energy storage market will reach US$223 billion in the next 20 years
According to estimates by the research firm IDTechEx, by the middle of this century, renewable energy sources such as solar power and wind power will increasingly become the world’s main source of electricity. Due to the variability in electricity generation provided by renewable energy sources, energy storage systems are needed to ensure a stable, balanced supply.
Demand response facilities, distributed battery storage, vehicle-to-grid technology, community-scale battery storage and other technologies will play a role in balancing a renewables-dominated grid. As these technologies develop, so does the need for long-duration energy storage (LDES) systems, which can typically store and dispatch electricity for six hours or more.
IDTechEx predicts in a research report that the global long-term energy storage market will reach US$ 223 billion by 2044. The report states that long-duration energy storage market growth will occur at different regional rates. For example, if California achieves its clean energy goals by 2035, it will increase the installed capacity of clean energy generation facilities deployed in 2035 by 280% compared to 2023. Other countries and states expected to see rapid growth in deployed renewable energy capacity include Germany, the United Kingdom, Italy, Australia, India and the United States, the report said.
“Increased penetration of renewable energy deployment will result in the need to dispatch energy over longer periods of time,” the report said.
IDTechEx says that once a country or region reaches about 45% of its energy mix with renewable electricity, durations of six hours or more will become the most cost-effective option. The report said global renewable energy generation will reach the 45% threshold by the 2030s, though popular markets will reach the milestone sooner.
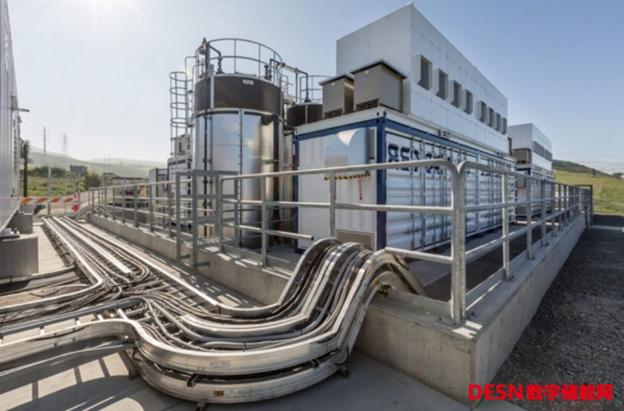
In addition to relying on local pumped water generation facilities, lithium-ion batteries dominate the global energy market, the report said. However, IDTechEx pointed out that the cost of using lithium-ion batteries to build long-term energy storage systems is too high.
To reduce costs, IDTechEx says redox flow batteries (RFB) can play this role.
” To increase the energy storage capacity of a redox flow battery (RFB), the size of the electrolyte storage tank can be increased,” the report said.
IDTechEx said that liquefied compressed air energy storage (LAES) is another cost-effective long-term energy storage technology.
The report states: “For liquefied compressed air energy storage (LAES), the size of the liquid – air storage tanks can increase. This results in the capital expenditure (on a USD /kWh basis) for many long-duration energy storage technologies increasing over the duration. Extended and faster non-linear decline.”
Other long-duration energy storage technologies evaluated in the rep), include iron-air batteries, zinc batteries (Zn-air , Zn-ion , Zn-MnO2 , Zn-Br) , high-temperature / molten salt batteries, and liquefied compressed air energy storage systems (LAES) , cryogenic / liquid carbon dioxide energy storage (LCES) , underground pumped hydro storage (APHS) , gravity energy storage systems (GESS) , thermal and electrothermal energy storage (TES) and (ETES) , and hydrogen energy facilities.
Source: ESCN